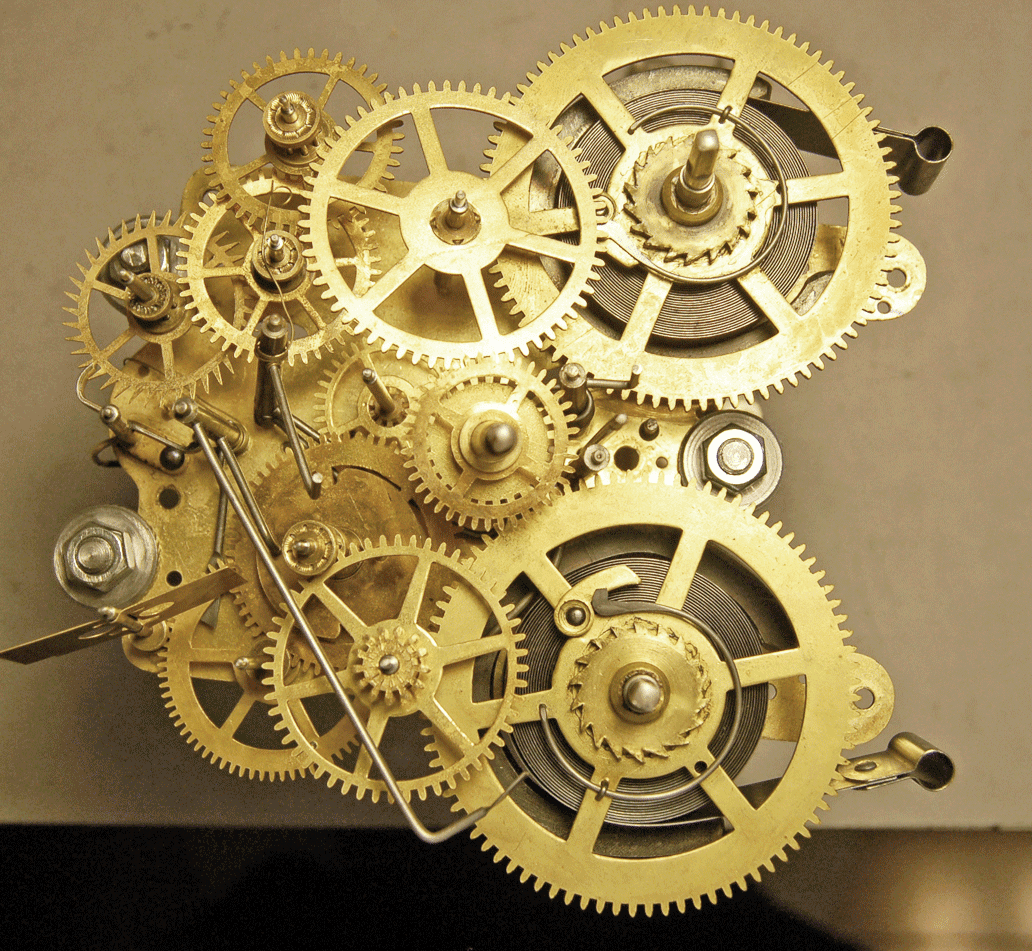
Clock workings are a fascinating subject that combines engineering, art, and science to help us keep track of time. From ancient sundials to modern digital watches, the evolution of timekeeping devices reflects humanity's quest for precision and reliability. In this article, we will delve into the intricate mechanisms behind clocks, explore different types of clock workings, and understand how they function to measure time accurately.
As we navigate through the various aspects of clock workings, we will uncover the history, components, and advancements in technology that have shaped the way we tell time. This comprehensive guide is designed for anyone interested in horology, whether you are a hobbyist, a professional, or simply curious about the inner workings of clocks.
By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of clock workings, their significance in our daily lives, and the craftsmanship involved in creating these remarkable devices. Let’s set the gears in motion and explore the fascinating world of timekeeping!
Table of Contents
- 1. History of Clock Workings
- 2. Key Components of Clocks
- 3. Different Mechanisms of Timekeeping
- 4. Types of Clocks
- 5. Modern Technology in Clock Making
- 6. Maintenance of Clocks
- 7. The Future of Timekeeping
- 8. Conclusion
1. History of Clock Workings
The journey of clock workings dates back thousands of years, with early civilizations developing methods to track time based on the position of celestial bodies. Here are some key milestones in the history of timekeeping:
- Ancient Sundials: The earliest timekeeping devices, sundials, utilized the sun's shadow to indicate the time of day.
- Water Clocks: Known as clepsydras, these devices measured time by the flow of water and were used in various cultures.
- Mechanical Clocks: The invention of mechanical clocks in the Middle Ages marked a significant advancement, allowing for more accurate timekeeping.
- Quartz Clocks: In the 20th century, quartz technology revolutionized clocks, providing unprecedented accuracy.
2. Key Components of Clocks
To understand clock workings, it is essential to familiarize ourselves with the main components that make up a clock:
- Escapement: This mechanism regulates the release of energy from the clock's mainspring, controlling the movement of the gears.
- Gear Train: A series of gears that transmit energy from the escapement to the hands of the clock, allowing them to move at the correct rate.
- Mainspring: A coiled spring that stores mechanical energy and powers the clock.
- Dial and Hands: The face of the clock displays the time, while the hands indicate the hours, minutes, and seconds.
2.1 The Role of the Pendulum
The pendulum, invented by Christiaan Huygens in the 17th century, became a crucial component in many mechanical clocks. It acts as a timekeeping element, swinging back and forth at a constant rate, which allows for precise measurement of time.
3. Different Mechanisms of Timekeeping
There are several mechanisms that clocks utilize to keep time, each with its own unique features:
- Mechanical Clocks: Rely on gears and springs, requiring manual winding to function.
- Quartz Clocks: Use a quartz crystal oscillator to regulate time, known for their accuracy and low maintenance.
- Atomic Clocks: The most precise timekeeping devices, utilizing the vibrations of atoms to measure time.
3.1 The Science Behind Quartz Clocks
Quartz clocks operate on the principle of piezoelectricity, where a quartz crystal generates a small voltage when subjected to mechanical stress. This property allows quartz clocks to maintain accurate time with minimal deviation.
4. Types of Clocks
Clocks come in various forms, each serving different purposes and aesthetic preferences:
- Wall Clocks: Common in homes and offices, these clocks provide time at a glance.
- Grandfather Clocks: Tall, freestanding clocks known for their intricate designs and pendulum mechanisms.
- Digital Clocks: Display time in numerical format, often with additional features like alarms and backlighting.
- Smartwatches: Combine traditional timekeeping with modern technology, offering notifications and health tracking.
4.1 Specialty Clocks
Some clocks are designed for specific functions, such as:
- Chronographs: Clocks that measure elapsed time and can function as stopwatches.
- World Clocks: Display time in different time zones, useful for travelers and global businesses.
5. Modern Technology in Clock Making
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced the clock industry, leading to innovative designs and functionalities:
- Smart Technology: Integration of smart technology allows clocks to connect to the internet, providing real-time updates and features like weather forecasting.
- Energy Efficiency: Solar-powered clocks and low-energy digital displays have become popular for their sustainability.
5.1 The Impact of 3D Printing
3D printing technology has revolutionized clock design, enabling custom components and intricate designs to be produced quickly and affordably.
6. Maintenance of Clocks
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and accuracy of clocks:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can affect the movement of clock mechanisms.
- Lubrication: Mechanical clocks require periodic lubrication to reduce friction between moving parts.
- Battery Replacement: For battery-operated clocks, timely battery replacement is crucial to maintain accurate timekeeping.
6.1 When to Seek Professional Help
If a clock shows signs of malfunction or requires complex repairs, it is advisable to consult a professional horologist for assistance.
7. The Future of Timekeeping
The future of clock workings is likely to be shaped by further technological advancements and changing consumer preferences:
- Wearable Technology: The rise of smartwatches and fitness trackers will continue to influence how we perceive time.
- Integration with Smart Homes: Clocks may increasingly become part of smart home ecosystems, synchronizing with other devices.
7.1 Sustainability in Clock Making
As environmental concerns grow, there will be a push towards more sustainable materials and practices in clock manufacturing.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding clock workings opens a window into the intricate world of timekeeping. From the historical evolution of clocks to modern technological advancements, each aspect contributes to the reliability and beauty of these devices. As we continue to innovate and adapt, the future of clock workings promises exciting developments that will enhance our experience of time.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments section below, share this article with fellow enthusiasts, and explore more on our website for additional fascinating insights into horology!
You Might Also Like
Task Force Engineer Assignment Overseas: A Comprehensive GuideFinal Cut Transitions Free: Enhance Your Video Editing Skills
Katana Asian: The Art, History, And Cultural Significance Of The Iconic Japanese Sword
Understanding Block Heels: The Perfect Blend Of Comfort And Style
Husband And Wife Plague Doctor Plush: A Unique Collectible For History Enthusiasts
Article Recommendations
- Southern Cornbread Recipe
- How To Make Live Edit Versions Of Pdf
- How To Get Rid Of Worry Dolls
- Take For Granted
- Lori Woodley
- Additional Shelf For Cabinets
- Winter Essentials Woman
- Best Forearm Workout Weight
- Karol G Tour
- Shield Recipe For Minecraft