Maintaining a good glucose level is crucial for overall health and well-being. Glucose, a simple sugar, is a primary source of energy for our bodies. Understanding what constitutes a good glucose level is essential, especially for individuals managing diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. This article will explore the optimal glucose levels, factors that influence blood sugar, and tips for maintaining healthy glucose levels.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the definitions of good glucose levels, how they vary by age and health status, and the implications of abnormal glucose readings. We aim to provide you with valuable insights backed by reputable sources to ensure informed decision-making about your health.
Whether you are looking to monitor your glucose levels for personal reasons or seeking information for someone else, this article will serve as a reliable resource to deepen your understanding of what a good glucose level looks like.
Table of Contents
- What is Glucose?
- Why Good Glucose Levels Matter
- Normal Glucose Levels
- Factors Affecting Glucose Levels
- How to Maintain Good Glucose Levels
- Monitoring Glucose Levels
- When to See a Doctor
- Summary
What is Glucose?
Glucose is a type of sugar that is found in the blood and is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. It is derived from the food we eat, particularly carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose during digestion. The body regulates glucose levels through the hormone insulin, which facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells.
Why Good Glucose Levels Matter
Maintaining good glucose levels is vital for several reasons:
- Energy Levels: Proper glucose levels ensure that your body has enough energy to function efficiently.
- Weight Management: Abnormal glucose levels can lead to weight gain or loss, affecting overall health.
- Prevention of Diabetes: Keeping glucose levels in check can help prevent type 2 diabetes.
- Overall Health: Stable glucose levels contribute to improved mood, cognitive function, and physical health.
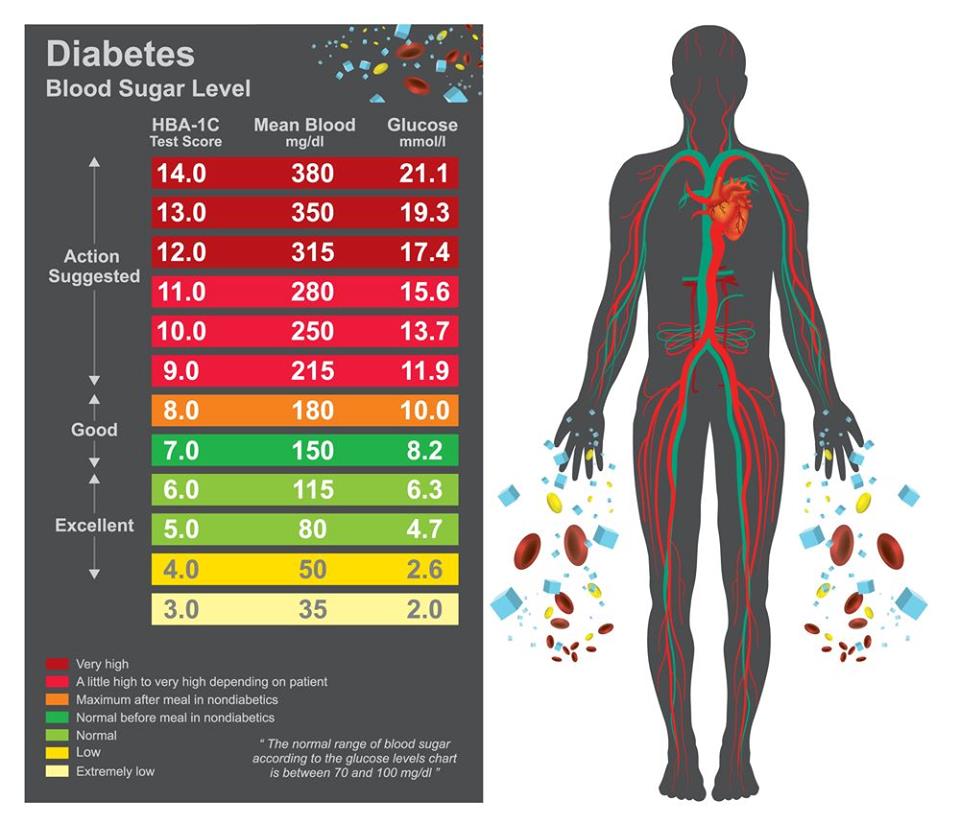
Normal Glucose Levels
Normal glucose levels can vary depending on several factors, including age, time of day, and whether a person has eaten. Here are the general guidelines:
| Measurement | Normal Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Fasting (8 hours without food) | 70-99 |
| Postprandial (2 hours after eating) | Less than 140 |
| Random | Less than 200 |
It is important to note that individual circumstances may vary. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Factors Affecting Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence glucose levels, including:
Diet
The types of food consumed play a significant role in glucose levels. High-carbohydrate meals can cause spikes in blood sugar, while a balanced diet can help maintain stable levels.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help regulate glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by muscles.
Stress and Hormones
Stress can lead to elevated glucose levels due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can affect insulin sensitivity.
Medical Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, hormonal disorders, and certain medications can also impact glucose levels.
How to Maintain Good Glucose Levels
Here are some effective strategies to help maintain good glucose levels:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Monitor Your Levels: Regularly check your glucose levels to ensure they remain within the normal range.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Monitoring Glucose Levels
Monitoring glucose levels is essential for those at risk of diabetes or managing the condition. Here are some common methods:
- Fingerstick Blood Test: A small drop of blood is tested using a glucose meter.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): A device worn on the skin that provides real-time glucose readings.
- A1C Test: A blood test that measures average glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of high or low blood sugar, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, or confusion, it is crucial to seek medical advice. Additionally, if your glucose levels remain consistently outside the normal range, a healthcare professional can provide guidance and support.
Summary
Maintaining a good glucose level is essential for overall health and well-being. The normal glucose ranges vary based on several factors, including fasting and post-meal measurements. To keep glucose levels stable, individuals should focus on a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management. Monitoring glucose levels and seeking medical advice when necessary can help manage risks associated with abnormal glucose levels.
Feel free to share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below! If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others or exploring more of our articles for additional health insights.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you again soon for more valuable health information.
You Might Also Like
Top Kids Movies: A Comprehensive Guide To The Best Family FilmsUnderstanding The Causes Of Dizziness In Women
Exploring The Leading Chewing Tobacco Brands: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Revelation 12: A Deep Dive Into Its Symbolism And Meaning
Its Going Down: Understanding The Impact Of Urban Culture And Society
Article Recommendations
- Exterior Joint Compound
- Nikki Minja Naked
- Business Tactics_0.xml
- How To Make Raphael In Infinite Craft
- Piper Parabo
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
- Digital Strategy_0.xml
- Bryan Hearne
- Talulah Riley
- Streaming Device Whose Name Means Six