Understanding how to find acceleration is crucial for students and professionals in the fields of physics, engineering, and various scientific disciplines. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. In this article, we will break down the concept of acceleration, explain how to calculate it, and provide examples to illustrate the process. Whether you are a student preparing for an exam or a professional needing a refresher, this guide aims to enhance your understanding of acceleration.
In the following sections, we will explore the various formulas used to find acceleration, discuss the different types of acceleration, and provide practical examples to solidify your comprehension. Additionally, we will touch upon real-world applications of acceleration in everyday life. By the end of this article, you will have a solid grasp of how to find acceleration and its relevance in the physical world.
Let’s dive into the world of acceleration and learn how to find it effectively!
Table of Contents
- 1. Definition of Acceleration
- 2. Types of Acceleration
- 3. Formulas to Find Acceleration
- 4. Practical Examples of Finding Acceleration
- 5. Real-World Applications of Acceleration
- 6. Conclusion
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Definition of Acceleration
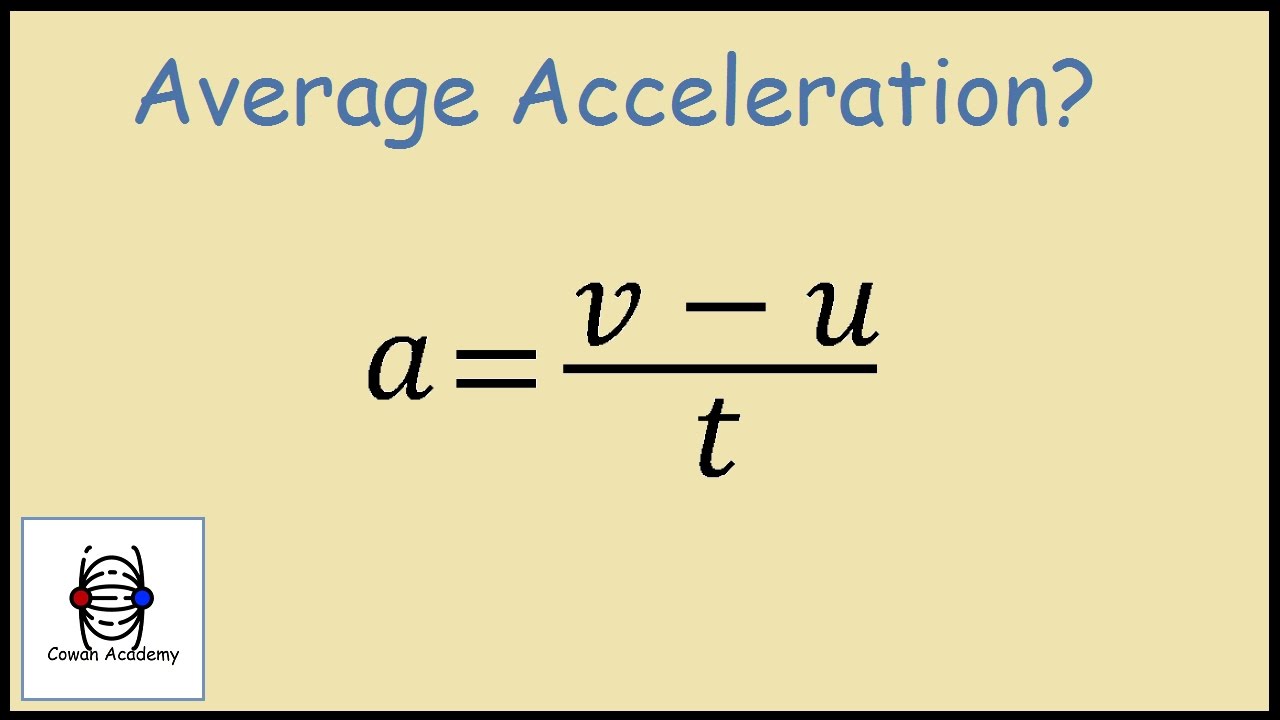
Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity per unit time. It can be expressed mathematically as:
a = (v_f - v_i) / t
Where:
- a = acceleration
- v_f = final velocity
- v_i = initial velocity
- t = time taken for the change in velocity
Acceleration is typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s²) in the International System of Units (SI).
2. Types of Acceleration
Acceleration can be classified into two main types: uniform and non-uniform acceleration.
2.1 Uniform Acceleration
Uniform acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity changes at a constant rate. For example, a car accelerating from a standstill to a higher speed at a steady rate exhibits uniform acceleration.
2.2 Non-Uniform Acceleration
Non-uniform acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity changes at a varying rate. An example of this is a car that speeds up and slows down while navigating through city traffic.
3. Formulas to Find Acceleration
There are several formulas available to find acceleration depending on the context of the problem.
3.1 Basic Acceleration Formula
As mentioned earlier, the basic formula to find acceleration is:
a = (v_f - v_i) / t
This formula is applicable in situations where you know the initial velocity, final velocity, and the time taken for the change in velocity.
3.2 Using Graphs to Find Acceleration
Acceleration can also be determined using velocity-time graphs. The slope of the line on a velocity-time graph represents acceleration. A steeper slope indicates a greater acceleration.
To find acceleration using a graph:
- Identify two points on the line: (t1, v1) and (t2, v2).
- Calculate the change in velocity (Δv = v2 - v1) and the change in time (Δt = t2 - t1).
- Use the formula: a = Δv / Δt.
4. Practical Examples of Finding Acceleration
Let's look at some practical examples to illustrate how to find acceleration.
Example 1: A car accelerates from 20 m/s to 50 m/s in 5 seconds.
Using the formula:
a = (v_f - v_i) / t = (50 m/s - 20 m/s) / 5 s = 6 m/s²
Example 2: A bike slows down from 15 m/s to 5 m/s in 4 seconds.
Using the formula:
a = (v_f - v_i) / t = (5 m/s - 15 m/s) / 4 s = -2.5 m/s²
The negative sign indicates that the bike is decelerating.
5. Real-World Applications of Acceleration
Acceleration is a fundamental concept that has numerous applications in real life:
- Transportation: Understanding vehicle acceleration helps in designing safer cars and improving fuel efficiency.
- Aerospace: Calculating acceleration is crucial in rocket launches and flight dynamics.
- Sports: Athletes can utilize acceleration data to improve their performance and training regimens.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to find acceleration is essential for students and professionals alike. By grasping the definitions, types, and formulas related to acceleration, you can apply this knowledge to various fields, including physics, engineering, and everyday life. Remember to practice with real-world examples to solidify your understanding. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts, please leave a comment below!
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What units are used to measure acceleration?
A1: Acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
Q2: Can acceleration be negative?
A2: Yes, negative acceleration is referred to as deceleration, which indicates a decrease in velocity.
Q3: How does gravity affect acceleration?
A3: Gravity provides a constant acceleration of approximately 9.81 m/s² towards the Earth, influencing the motion of falling objects.
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on how to find acceleration. We hope you found it informative and helpful. Don’t forget to check out our other articles for more insights into physics and other scientific topics!
You Might Also Like
Exploring The Diverse Types Of Comedy: A Comprehensive GuideUnderstanding The Foil Method: A Comprehensive Guide
Top Reasons For Divorce: Understanding The Factors Behind Marital Breakdowns
Understanding Code Phone 44: What You Need To Know
Creative Birthday Present Ideas To Make Their Day Special
Article Recommendations
- Cast Of Hidden Figures
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Debutante
- Mary Anne Macleod Trump
- Deacon Johnson
- Piper Parabo
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Business Resilience_0.xml
- How Old Is Adriana Lima 2024
- Convert Excel To Html Table