When it comes to manufacturing processes, understanding the difference between molding and casting is crucial for anyone involved in production, design, or engineering. Both techniques are widely used in various industries to create parts and products, but they employ different methods and materials. This article will explore the nuances of molding and casting, helping you to determine which method is best suited for your project needs.
The world of manufacturing can be complex, especially when choosing the right techniques for your applications. Molding and casting are two processes that may seem similar, but they have distinct differences that can significantly impact the quality and characteristics of the final product. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of each process, their advantages and disadvantages, and practical applications to guide you in your decision-making.
By understanding the differences between molding and casting, you will be better equipped to select the appropriate method for your manufacturing needs. Whether you're creating prototypes, mass-producing items, or designing unique components, knowing when to use molding or casting can save time, resources, and improve the overall quality of your products.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is Molding?
- 2. What is Casting?
- 3. Key Differences Between Molding and Casting
- 4. Advantages of Molding
- 5. Advantages of Casting
- 6. Applications of Molding and Casting
- 7. Choosing Between Molding and Casting
- 8. Conclusion
1. What is Molding?
Molding is a manufacturing process that involves creating a hollow cavity in a mold, into which a material is poured or injected to form a specific shape. The mold is typically made of hard materials like metal or plastic, and the material used can vary from plastics to metals, depending on the application.
There are several types of molding processes, including:
- Injection Molding: A process where molten material is injected into a mold under high pressure.
- Blow Molding: Used primarily for producing hollow objects by inflating a heated plastic tube.
- Compression Molding: Involves placing a material into an open mold, which is then closed and heated to shape the material.
- Thermoforming: A process where plastic is heated and then formed over a mold.
2. What is Casting?
Casting is another manufacturing technique where a liquid material is poured into a mold and allowed to solidify. The mold can be made of various materials, including sand, metal, or ceramic, and can be reused or single-use depending on the casting method.
Common casting processes include:
- Sand Casting: Involves creating a mold from sand and pouring liquid metal into it.
- Die Casting: A high-pressure process that forces molten metal into a mold cavity.
- Investment Casting: Also known as lost-wax casting, where a wax pattern is coated with a ceramic material, and then the wax is melted away.
- Continuous Casting: A process where molten metal is continuously poured into a mold to produce long shapes.
3. Key Differences Between Molding and Casting
While both molding and casting are used to create parts and products, they differ in several fundamental ways:
- Process: Molding typically involves injecting or pouring materials into a mold, while casting involves pouring liquid materials into a mold to solidify.
- Materials: Molding is often used for plastics and some metals, whereas casting is primarily used for metals and alloys.
- Mold Reusability: Molds for molding processes can often be reused multiple times, while casting molds may be single-use or reusable, depending on the method.
- Complexity: Molding can create more intricate designs due to the nature of injection and blow molding, while casting is typically used for simpler shapes.
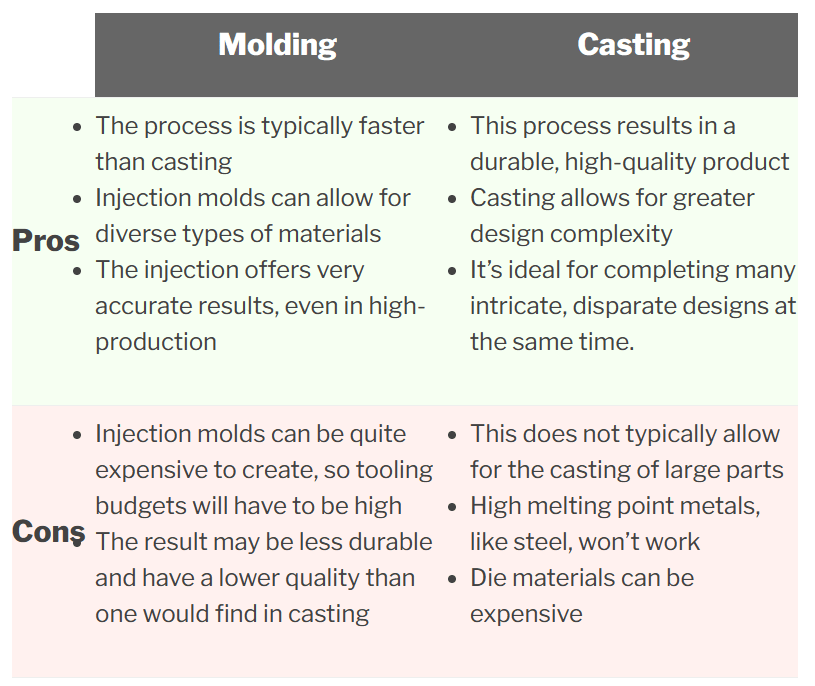
4. Advantages of Molding
Molding offers several benefits that make it a popular choice in manufacturing:
- High Production Rates: Molding processes, especially injection molding, can produce a large number of parts quickly.
- Precision and Consistency: Molding allows for high precision and consistency in part dimensions.
- Material Variety: A wide range of materials can be used in molding processes, including thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics.
- Cost-Effective for Large Runs: Once the mold is created, the cost per part decreases significantly in large production runs.
5. Advantages of Casting
Casting also has its own set of advantages:
- Complex Shapes: Casting can create complex shapes that may be difficult or impossible to achieve with molding.
- Material Versatility: A variety of metals and alloys can be used, offering different mechanical properties.
- Low Tooling Costs: The initial cost for creating casting molds, particularly sand molds, can be lower than for molding.
- Ability to Handle High Temperatures: Casting is suitable for high-temperature materials, making it ideal for metals.
6. Applications of Molding and Casting
Both molding and casting have diverse applications across various industries:
- Molding Applications:
- Automotive parts
- Consumer products
- Medical devices
- Packaging materials
- Casting Applications:
- Engine blocks
- Machine components
- Art sculptures
- Jewelry
7. Choosing Between Molding and Casting
When deciding between molding and casting, consider the following factors:
- Production Volume: Molding is more cost-effective for high-volume production, while casting may be better for lower volumes or one-off items.
- Material Requirements: If you need a specific material property, choose the method that best suits your needs.
- Complexity of Design: Consider the complexity of your design and which method can best achieve it.
- Budget: Assess your budget for tooling and production costs, as this can influence your choice.
8. Conclusion
In summary, understanding the difference between molding and casting is essential for making informed decisions in manufacturing. Each method has its own advantages and is suitable for different applications. By evaluating your project requirements, you can choose the right technique that aligns with your needs.
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment below, share it with others, or explore more articles on our site to enhance your knowledge about manufacturing processes.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more insightful content!
You Might Also Like
Understanding The Twice Stabbed Lady Beetle: Are They Poisonous?Ultimate Guide To Destiny 2 Fishing Tackle: Mastering The Art Of Fishing In The Game
Understanding Negative Drop Shoes: Benefits, Drawbacks, And Recommendations
How Much Is Alexandrite? A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Alexandrite Pricing
Mike Huckabee And Relaxium Sleep: A Comprehensive Guide To Better Sleep
Article Recommendations
- Air Conditioning Compressor
- Is Blocking Considered Cheesing In Fromsoft Games
- Toy Robot Dogs
- Winter Essentials Woman
- Take For Granted
- Fan Sound
- Street Taco Recipe
- Forest Sunlight
- Wicker Outdoor Furniture
- Whats Akons Real Name