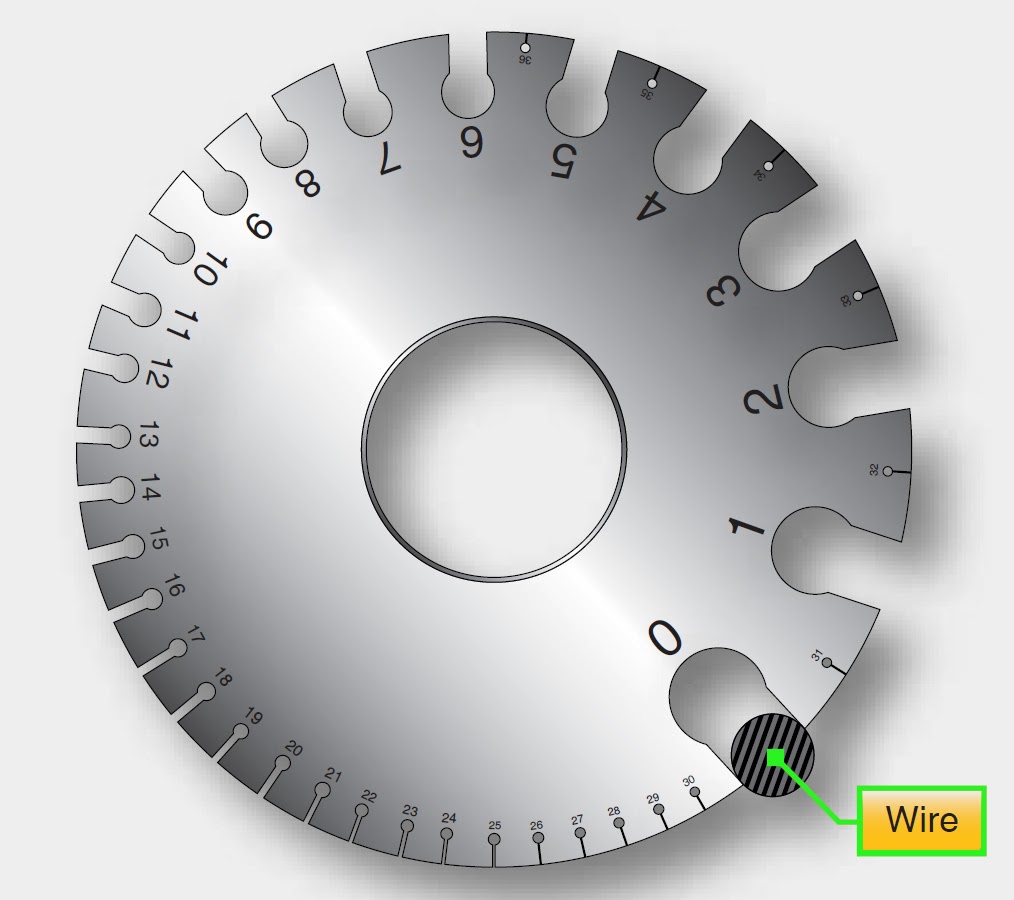
Wire gauge is a critical aspect of electrical wiring that affects performance, safety, and compatibility. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of wire gauge, exploring its importance, types, and applications in various fields. Whether you’re an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, or simply curious about electrical systems, understanding wire gauge is vital for ensuring optimal performance and safety in electrical installations.
In this article, we will cover everything from the basics of wire gauge measurement to its specific applications in different industries. We will also touch on how to choose the right wire gauge for your projects and the implications of using the wrong gauge. By the end of this guide, you will have a well-rounded understanding of wire gauge and its relevance in electrical work.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of wire gauge and uncover the essential knowledge that will empower you in your electrical endeavors. From definitions and measurements to practical applications and safety guidelines, this article is designed to be a go-to resource for all things related to wire gauge.
Table of Contents
- What is Wire Gauge?
- Types of Wire Gauge
- How to Measure Wire Gauge
- Applications of Wire Gauge
- Choosing the Right Wire Gauge
- Consequences of Using the Wrong Gauge
- Safety Considerations
- Conclusion
What is Wire Gauge?
Wire gauge refers to the standardized system used to measure the diameter of electrical wires. The wire gauge determines the amount of electrical current that can safely pass through the wire without overheating. In simpler terms, wire gauge is crucial for ensuring that electrical systems operate efficiently and safely.
The gauge number is inversely related to the wire diameter; as the gauge number increases, the diameter of the wire decreases. This means that a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire capable of carrying more current, while a higher gauge number refers to thinner wires that can carry less current.
Types of Wire Gauge
American Wire Gauge (AWG)
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) is the most common wire gauge system used in North America. It was developed in the 1850s and has become the standard for measuring wire diameters in electrical applications. The AWG system uses a series of numbers, with 00 (or 2/0) being the thickest and 40 being the thinnest.
Standard Wire Gauge (SWG)
The Standard Wire Gauge (SWG) is primarily used in the United Kingdom and other countries that follow British standards. Similar to the AWG system, the SWG system measures wire diameter in a way that a lower number indicates a thicker wire. However, the SWG measurements differ from AWG, and thus, it is important to choose the correct gauge system based on the region.
How to Measure Wire Gauge
Measuring wire gauge can be done using several methods, including:
- Wire Gauge Tool: The most accurate way to measure wire gauge is to use a wire gauge tool, which is specifically designed for this purpose.
- Calipers: Digital calipers can also be used to measure the diameter of the wire accurately.
- AWG Chart: You can refer to an AWG chart that lists the diameter and current-carrying capacity for various gauge numbers.
Applications of Wire Gauge
Residential Wiring
In residential wiring, different wire gauges are used for various circuits. For example:
- 14 AWG is commonly used for lighting circuits.
- 12 AWG is used for general-purpose outlets.
- 10 AWG is often used for air conditioning units and larger appliances.
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, wire gauge plays a crucial role in machinery and equipment. Thicker wires are often needed to support higher currents, while thinner wires may be used for low-power applications. Proper wire gauge selection is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring safe operation.
Choosing the Right Wire Gauge
Choosing the appropriate wire gauge involves considering several factors:
- Current Load: Determine the maximum current that will pass through the wire to select a gauge that can handle the load.
- Distance: Consider the distance the electricity needs to travel, as longer distances may require thicker wires to reduce voltage drop.
- Application: Evaluate the specific application and environmental conditions that may affect wire performance.
Consequences of Using the Wrong Gauge
Using the wrong wire gauge can lead to several serious consequences:
- Overheating: Wires that are too thin for the current load can overheat, leading to insulation failure and potential fire hazards.
- Voltage Drop: Thinner wires can cause significant voltage drop over long distances, resulting in inefficient operation of electrical devices.
- Equipment Damage: Appliances and machinery may suffer damage if they do not receive the proper voltage due to inadequate wiring.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when working with electrical wiring. Here are some important safety tips to consider:
- Always use the appropriate wire gauge for the specific application.
- Inspect wires regularly for signs of wear or damage.
- Follow local electrical codes and regulations when installing or replacing wiring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding wire gauge is crucial for anyone involved in electrical work. The wire gauge affects not only the performance and efficiency of electrical systems but also their safety. By choosing the right wire gauge and adhering to safety guidelines, you can ensure that your electrical installations are reliable and safe.
We encourage you to leave your comments or questions below and share this article with others who may find it helpful. Additionally, feel free to explore other informative articles on our site to expand your knowledge further.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you back here for more insightful content!
You Might Also Like
Best Restaurants In Clearwater: A Culinary JourneyExploring Hawaii Snorkeling: A Comprehensive Guide To Underwater Adventures
Ultimate Guide To Denim Outfit: Styling Tips And Trends
Saber Vs Conocer: Understanding The Difference Between Two Spanish Verbs
Understanding Fitment: A Comprehensive Guide To Vehicle Fitment And Its Importance
Article Recommendations
- Kylie Jenner Before Surgery
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Kamila Valieva
- Daryl Hannah
- Lava Stone Bracelet Essential Oil
- Collision Repair Before And After
- Efficient Strategies_0.xml
- Business Resilience_0.xml
- 76 Out Of 80
- Claudine Blanchard Crimes
.png/1200px-Wire_gauge_(PSF).png)