Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental aspect of our universe that influences a wide range of technologies and natural phenomena. From the light we see to the radio waves that allow us to communicate, understanding electromagnetic waves is crucial for grasping modern science and technology. This article delves deep into the properties, types, and applications of electromagnetic waves, making it an essential read for students, professionals, and anyone interested in the sciences.
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. As we explore this topic, we will discuss the scientific principles underlying electromagnetic waves, their practical applications in everyday life, and the ongoing research that continues to shape our understanding of this essential phenomenon.
Join us as we navigate through the intricate world of electromagnetic waves, exploring their significance in communication, medicine, and other fields. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of electromagnetic waves and their importance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Table of Contents
- What are Electromagnetic Waves?
- Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
- Types of Electromagnetic Waves
- Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
- The Science Behind Electromagnetic Waves
- Health Impacts of Electromagnetic Waves
- The Future of Electromagnetic Wave Research
- Conclusion
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic waves are waves of energy that travel through space at the speed of light. They are generated by the movement of charged particles and are composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Understanding electromagnetic waves is crucial for various fields, including physics, engineering, and telecommunications.
These waves can propagate through a vacuum as well as through various media, making them versatile in their applications. The fundamental equation governing the behavior of electromagnetic waves is Maxwell's equations, which describe how electric and magnetic fields interact and propagate.
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
The properties of electromagnetic waves include:
- Speed: All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second).
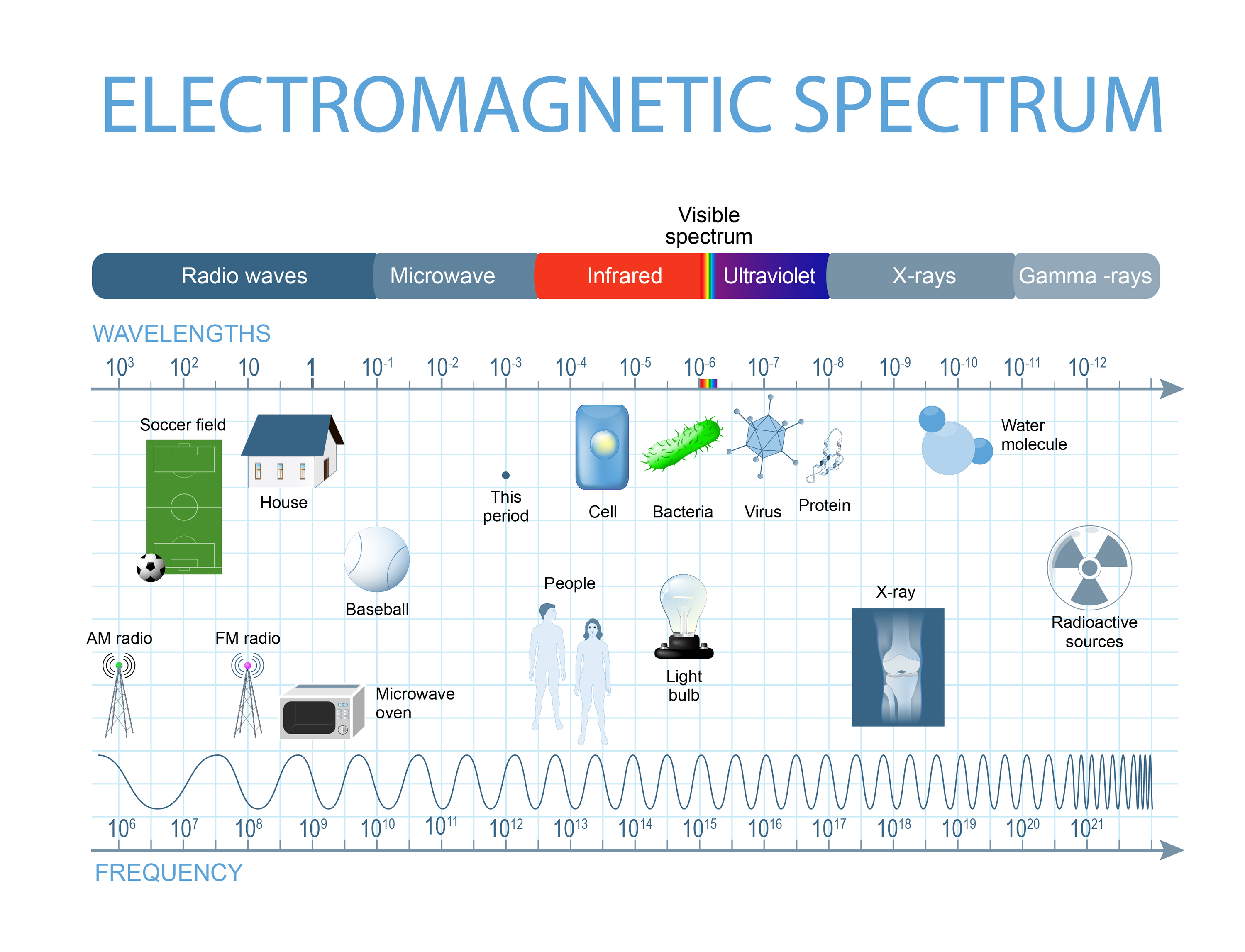
- Wavelength: The distance between successive peaks of the wave. Wavelengths can range from less than a millimeter (gamma rays) to thousands of kilometers (radio waves).
- Frequency: The number of wave cycles that pass a point in one second, measured in hertz (Hz). Higher frequencies correspond to shorter wavelengths.
- Amplitude: The height of the wave, which is related to the energy carried by the wave. Greater amplitude means higher energy.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves can be classified into different types based on their wavelengths and frequencies:
- Radio Waves: Used for communication; they have the longest wavelengths (from a few millimeters to kilometers).
- Microwaves: Employed in cooking and satellite transmissions; wavelengths range from 1 millimeter to 1 meter.
- Infrared Waves: Experienced as heat; wavelengths range from 700 nanometers to 1 millimeter.
- Visible Light: The small portion of the spectrum visible to the human eye; wavelengths range from approximately 400 to 700 nanometers.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Rays: Beyond visible light; can cause sunburn; wavelengths range from 10 to 400 nanometers.
- X-rays: Used in medical imaging; wavelengths range from 0.01 to 10 nanometers.
- Gamma Rays: Emitted by radioactive materials; they have the shortest wavelengths (less than 0.01 nanometers).
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves have numerous applications across various fields:
1. Communication
Electromagnetic waves are the backbone of modern communication systems, including:
- Television and Radio Broadcasting
- Mobile Phone Networks
- Satellite Communications
2. Medical Imaging
In the medical field, electromagnetic waves play a vital role in diagnostic imaging:
- X-ray Imaging
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasound Imaging
3. Industrial Applications
Electromagnetic waves are also used in various industrial applications:
- Microwave Heating in Food Processing
- Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring
- Non-Destructive Testing of Materials
The Science Behind Electromagnetic Waves
The behavior of electromagnetic waves can be explained through Maxwell's equations, which consist of four fundamental equations that describe how electric and magnetic fields interact. These equations illustrate that a changing electric field generates a magnetic field, and vice versa, leading to the propagation of electromagnetic waves.
Moreover, the wave-particle duality concept suggests that electromagnetic waves exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, which is fundamental in quantum mechanics.
Health Impacts of Electromagnetic Waves
Concerns regarding the health impacts of electromagnetic waves have been a topic of debate, especially in relation to:
- Cell Phone Radiation
- Electromagnetic Field Exposure from Power Lines
- Long-term Effects of UV Exposure
Research continues to explore these impacts, emphasizing the importance of understanding safe exposure levels and the potential risks associated with various forms of electromagnetic radiation.
The Future of Electromagnetic Wave Research
As technology evolves, so does the research surrounding electromagnetic waves. Future areas of exploration include:
- Advancements in Wireless Communication Technologies
- Improved Medical Imaging Techniques
- Research on the Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation on Health
These developments will continue to shape our understanding and applications of electromagnetic waves in the years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves are integral to our everyday lives, influencing communication, medicine, and technology. Understanding their properties, types, and applications is essential for leveraging their potential and mitigating associated risks. As research progresses, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments in this fascinating field.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article, or explore more articles on our site to further enhance your knowledge of electromagnetic waves and their significance in our world.
References
- Maxwell, J. C. (1864). A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field.
- Feynman, R. P. (1964). The Feynman Lectures on Physics.
- World Health Organization. (2020). Electromagnetic Fields and Public Health.
- National Institute of Health. (2021). Health Effects of Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields.
You Might Also Like
Small Trucks: The Ultimate Guide To Choosing The Right One For Your NeedsDiscover The Best Massage In Austin: A Complete Guide
Discovering Veal Chop: A Culinary Delight
Perfect Is The Enemy Of Good: Embracing Imperfection For Success
Best Work Boots: Your Ultimate Guide To Comfort And Safety
Article Recommendations
- How Tall Sarah Jessica Parker
- Future Opportunities_0.xml
- Long Handled Post Hole Diggers
- Career Advancement_0.xml
- Data Driven_0.xml
- Sheryl Lowe Age
- Clr Soak Overnight
- Hig Roberts
- Lax Plane Spotting Locations
- Global Impact_0.xml