Cartridge anatomy is an essential aspect of understanding how firearms operate and ensuring safe handling and maintenance. In the realm of firearms, the cartridge is a critical component that directly influences performance, reliability, and safety. This article will delve deep into the anatomy of cartridges, exploring their various components, types, and functions. We aim to provide a thorough understanding that not only informs but also empowers firearm enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Understanding cartridge anatomy is vital for anyone involved in shooting sports, hunting, or firearms maintenance. Knowing the intricacies of each component can enhance your shooting experience, improve accuracy, and ensure safety. In this guide, we will take a closer look at the anatomy of cartridges, detailing each component's role and function, and providing insights into the different types available in the market.
As we navigate through the details of cartridge anatomy, we will also highlight important safety considerations and maintenance tips. Whether you are a seasoned shooter or a beginner, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge necessary to appreciate the complexities of cartridges.
Table of Contents
- What is a Cartridge?
- Components of a Cartridge
- Types of Cartridges
- Understanding Caliber
- Cartridge Manufacturing Process
- Cartridge Safety Considerations
- Maintaining Your Cartridges
- Conclusion
What is a Cartridge?
A cartridge is a complete unit of ammunition designed for use in firearms. It typically comprises several key components that work together to facilitate the firing process. Understanding what a cartridge is and how it functions is crucial for anyone interested in firearms.
Components of a Cartridge
There are several essential components that make up a cartridge:
- Case: The outer shell that holds all the components together.
- Primer: A small explosive device that ignites the gunpowder when struck by the firing pin.
- Gunpowder: The propellant that creates the gas needed to propel the projectile.
- Projectile: The bullet or shot that is expelled from the firearm when the cartridge is fired.
Detailed Examination of Each Component
Let’s take a closer look at each component:
Case
The case is typically made of brass, steel, or aluminum and serves to contain the primer, gunpowder, and projectile. It also provides a seal to prevent gas from escaping during firing.
Primer
Primers are usually made of a small metal cup filled with a sensitive explosive material. When the firing pin strikes the primer, it ignites, sending a flame into the case to ignite the gunpowder.
Gunpowder
Gunpowder (or smokeless powder) is the propellant that generates gas when ignited. This gas expands rapidly, creating pressure that propels the projectile down the barrel of the firearm.
Projectile
The projectile is the actual bullet or shot that exits the barrel and is intended to hit a target. Projectiles come in various shapes and sizes, depending on their intended use.
Types of Cartridges
Cartridges can be categorized in several ways, including:
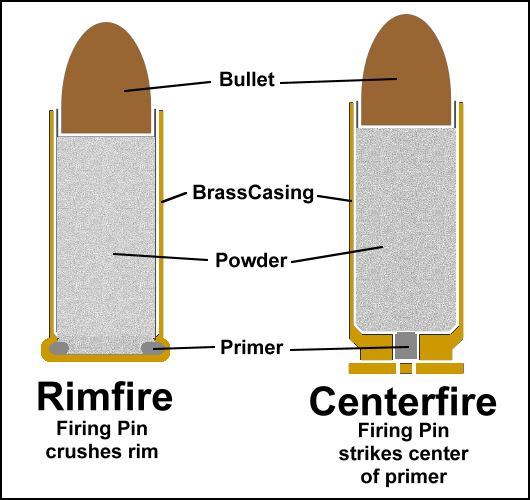
- Rimfire vs. Centerfire: Rimfire cartridges have the primer located in the rim, while centerfire cartridges have the primer in the center of the case base.
- Shotgun Shells vs. Rifle Cartridges: Shotgun shells are designed for smoothbore firearms and usually contain multiple pellets, while rifle cartridges are designed for rifled barrels and contain a single projectile.
- Standard vs. Magnum: Magnum cartridges contain more gunpowder than standard cartridges, resulting in higher velocity and energy.
Understanding Caliber
Caliber refers to the diameter of the firearm's bore or the diameter of the projectile. It is an important factor in selecting ammunition for a firearm.
- Common Caliber Measurements: Calibers can be measured in inches (e.g., .45 ACP) or millimeters (e.g., 9mm).
- Impact of Caliber on Performance: Different calibers produce different levels of recoil, velocity, and energy, affecting accuracy and terminal performance.
Cartridge Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of cartridges involves several steps:
- Manufacturing the case from brass, steel, or aluminum.
- Inserting the primer into the case.
- Adding the appropriate amount of gunpowder.
- Seating the projectile into the case.
- Quality control testing to ensure safety and reliability.
Cartridge Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when handling cartridges. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Always store cartridges in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Inspect cartridges for damage or corrosion before use.
- Never attempt to disassemble cartridges or reload them unless you are trained and knowledgeable.
Maintaining Your Cartridges
Proper maintenance of cartridges can enhance their longevity and performance:
- Store cartridges in their original packaging or a dedicated ammunition box.
- Avoid exposing cartridges to moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Regularly check for signs of damage or wear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding cartridge anatomy is essential for anyone involved in shooting sports or firearms handling. By familiarizing yourself with the components, types, and safety considerations, you can improve your shooting experience and ensure safe practices. We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with fellow enthusiasts, and explore other related articles on our site.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you back on our site for more informative content!
You Might Also Like
Wash In Wash Out Hair Dye Brown: The Ultimate Guide For Effortless Hair Color ChangeBest Protein Powder Without Artificial Sweeteners: A Comprehensive Guide
Thinning Acrylic Latex Paint For Spraying: A Comprehensive Guide
Embrace Your Style: The Ultimate Guide To Hippie Clothing For Men
Hero Vs Anti-Hero: Understanding The Thin Line Between Good And Evil
Article Recommendations
- Saturnalia And Christmas
- Crayola Crayon Drawing
- 666
- Net Worth Of Samuel Jackson
- Cut Grass With Shears
- 150 Yards In Feet
- Ubuntu Install Deb File Command Line
- Best Bbq In Denver
- Medicated Shampoo For Scabs On Scalp
- Adhd And Gaming