Understanding how to find molar mass is essential for students, chemists, and anyone interested in the science of matter. Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us convert between grams of a substance and the number of moles, which is crucial for stoichiometric calculations. In this article, we will explore what molar mass is, how to calculate it, and its significance in various chemical applications.
The concept of molar mass is not only vital for academic purposes but also plays a significant role in real-life applications, such as pharmaceuticals, cooking, and environmental science. Knowing how to find molar mass allows scientists and engineers to predict how substances will react with one another, making it a cornerstone of chemical education and practice.
This guide will provide you with a step-by-step process for calculating molar mass, along with useful tips and examples to enhance your understanding. We will also discuss how molar mass is used in different fields and why it is important for both theoretical and practical chemistry.
Table of Contents
- What is Molar Mass?
- Importance of Molar Mass
- How to Calculate Molar Mass
- Molar Mass in Chemistry
- Applications of Molar Mass
- Common Molar Masses
- Troubleshooting Molar Mass Calculations
- Conclusion
What is Molar Mass?
Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. It is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is numerically equivalent to the molecular weight of a compound. The molar mass of a substance can be determined by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms present in its molecular formula.
Importance of Molar Mass
Molar mass plays a critical role in various aspects of chemistry, including:
- Stoichiometry: Molar mass is essential for converting between grams and moles, which is necessary for stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions.
- Solution Preparation: Knowing the molar mass allows chemists to prepare solutions with precise concentrations.
- Pharmaceuticals: Accurate dosing of medications often relies on understanding molar mass.
- Environmental Science: Molar mass helps in assessing the impact of pollutants and their concentrations in the environment.
How to Calculate Molar Mass
Calculating molar mass involves a straightforward process that can be broken down into a few simple steps:
Using the Periodic Table
1. **Identify the Compound:** Start with the chemical formula of the compound.
2. **List the Elements:** Write down all the elements present in the compound.
3. **Find Atomic Masses:** Use the periodic table to find the atomic mass of each element.
4. **Count Atoms:** Count how many atoms of each element are present in the chemical formula.
5. **Calculate Total Mass:** Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element, and then sum all these values to get the total molar mass.
Example Calculation
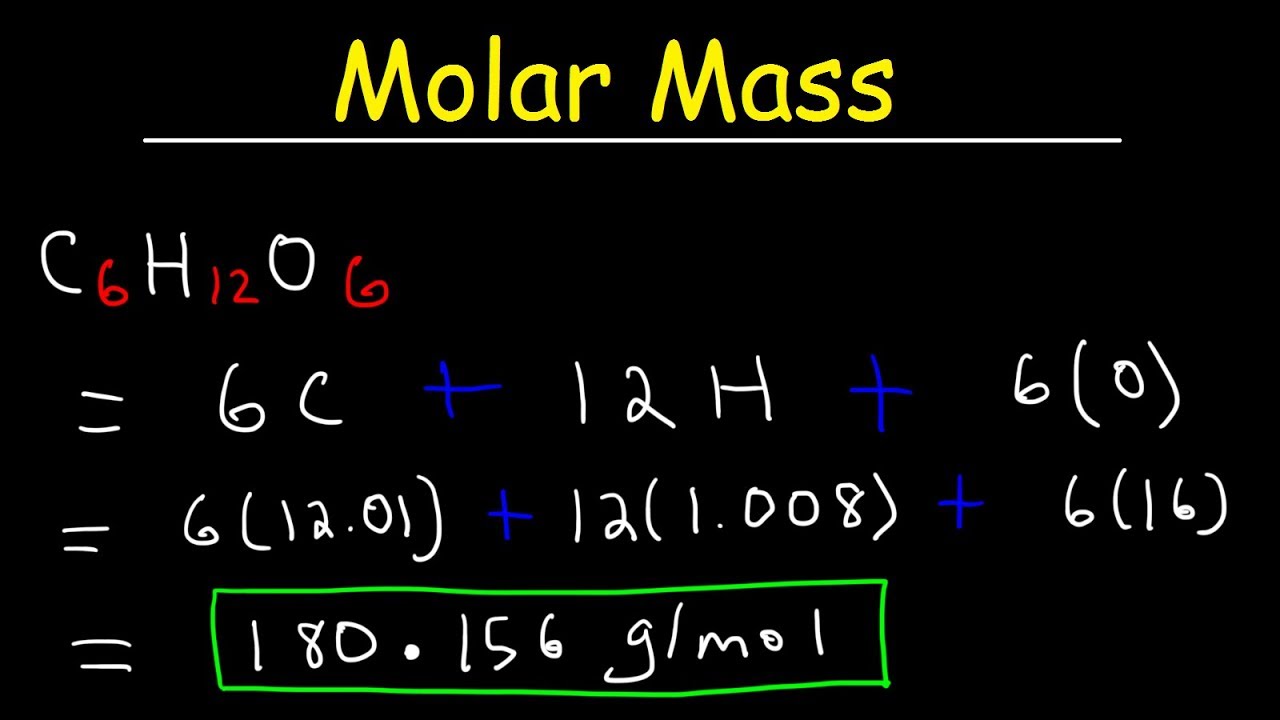
Let’s calculate the molar mass of water (H₂O):
- Hydrogen (H): 2 atoms × 1.01 g/mol = 2.02 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 1 atom × 16.00 g/mol = 16.00 g/mol
Total Molar Mass of H₂O: 2.02 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol = 18.02 g/mol
Molar Mass in Chemistry
Molar mass is foundational in various branches of chemistry, including organic, inorganic, and physical chemistry. It is used to:
- Determine reactant and product quantities in chemical reactions.
- Calculate yields and purities in synthetic reactions.
- Understand gas laws and behaviors in physical chemistry.
Applications of Molar Mass
Beyond theoretical applications, molar mass is crucial in practical scenarios:
- Pharmaceuticals: Accurate dosing based on molar mass ensures the efficacy of medications.
- Food Science: Molar mass is important for understanding the composition of food and nutritional information.
- Environmental Chemistry: Analyzing pollutants and their concentrations in air and water quality assessments.
Common Molar Masses
Here are some common compounds and their molar masses:
| Compound | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|
| Water (H₂O) | 18.02 |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | 44.01 |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | 58.44 |
| Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) | 180.18 |
Troubleshooting Molar Mass Calculations
If you encounter difficulties in calculating molar mass, consider the following tips:
- Double-check the chemical formula for accuracy.
- Ensure you are using the correct atomic masses from the periodic table.
- Pay attention to the number of each type of atom in the formula, particularly for polyatomic ions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to find molar mass is not just an academic exercise but a vital skill in various fields, from chemistry to environmental science. By mastering the calculation of molar mass, you can enhance your ability to engage with scientific problems and real-world applications.
We encourage you to practice calculating molar masses for different compounds and to explore their significance in your daily life. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below!
Thank you for reading our comprehensive guide on how to find molar mass. We hope you found it informative and useful!
You Might Also Like
Understanding 30 Percent Body Fat: What It Means For Your HealthStar Necklace: The Timeless Accessory That Shines Bright
Spoonful Of Sugar Song: The Timeless Classic That Inspires Joy
Creative Names For A Black Female Puppy: A Comprehensive Guide
Top Restaurants For Birthday Dinner Near Me: Celebrate In Style
Article Recommendations
- Sheryl Lowe Age
- Digital Revolution_0.xml
- Convert Excel To Html Table
- 76 Out Of 80
- Global Impact_0.xml
- Chevy S10 Steering Wheel
- How Tall Sarah Jessica Parker
- How Old Is Miguel Diaz
- Wallet With Pull Tab
- Streaming Device Whose Name Means Six